Orientation Tools
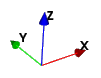
Figure 29 Orientation Tool
Through this panel (Figure 30) it is possible to set the properties of the object shown in Figure 29. It shows the orientation of the 3 axes (X, Y and Z) in the 3D space.
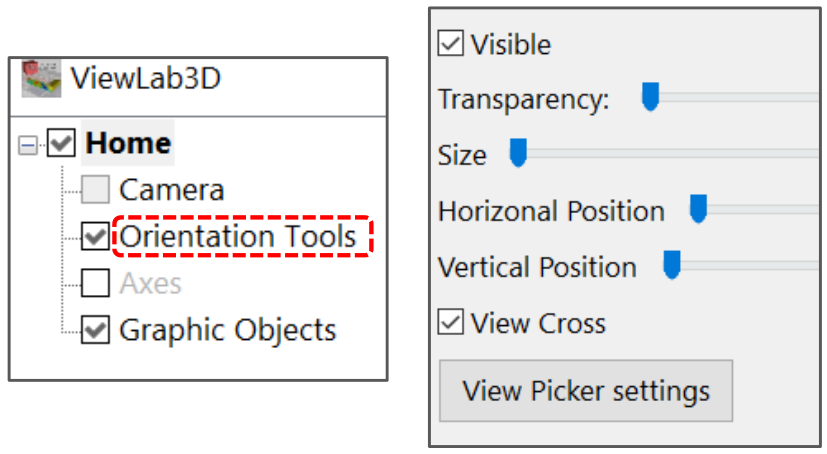
Figure 30 Orientation Tools panel
Visible
Allows to visualize the object or not, depending on if the box is checked.
Transparency
Allows the transparency of the object to be set. When the slider is totally at left the object is completely visible. When it is on the right it is not visible at all, totally transparent, and at intermediate positions it is more transparent as the slide goes towards the right, as shown in Figure 31.
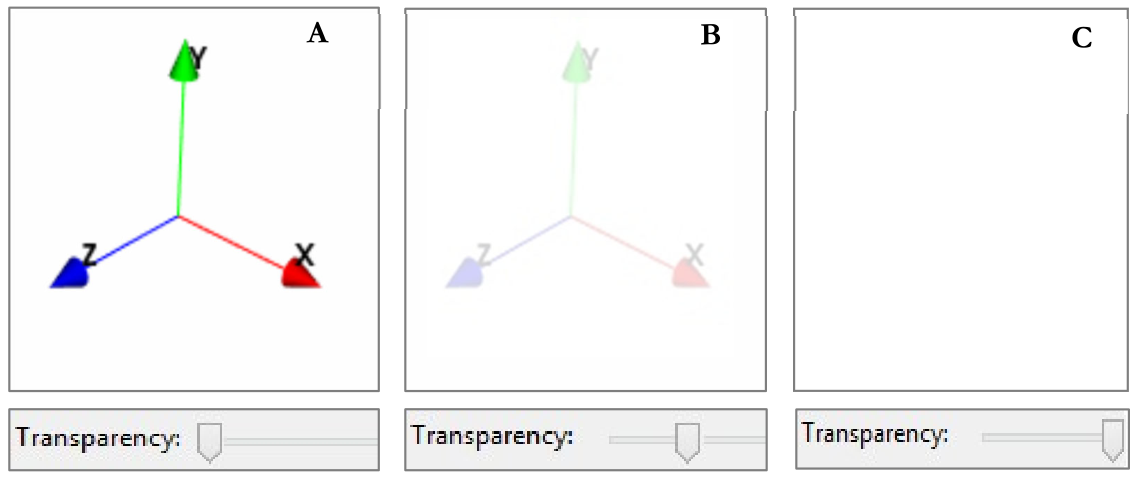
Figure 31 Different level of transparency of the object. In A the transparency is set at the minimum (in the detail the axes are completely visible), in B the transparency is set at an intermediate level (in the detail the axes are semi-transparent) and in C the transparency is set at the maximum level (in the detail the axes are not visible at all)
Size
Allows the size of the object to change. Between a maximum (slide at right) and a minimum (slide at left) depending on the position of the slider.
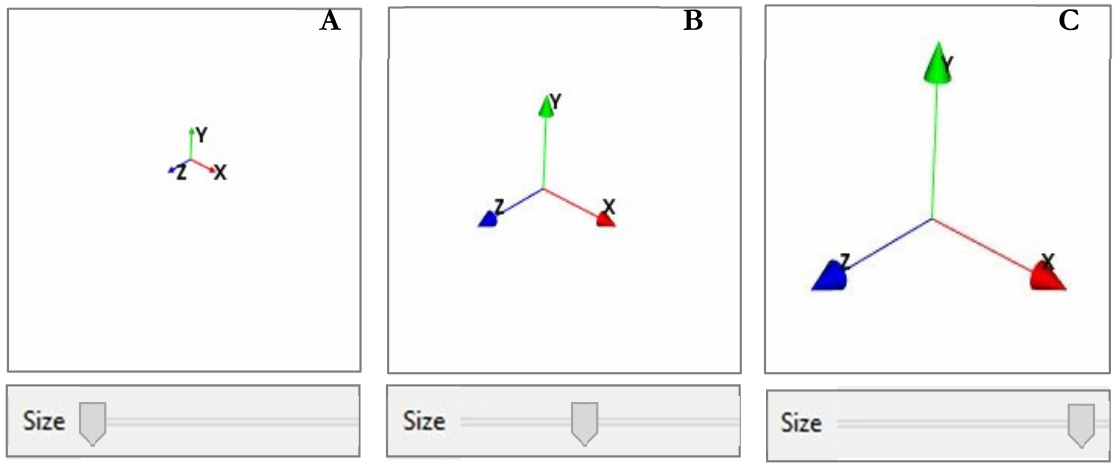
Figure 32 Different sizes of the orientation tool; in A minimum size, in B an intermediate size and in C maximum size
Horizontal Position
Allows to select the horizontal position of the Orientation Tool, between a maximum left side (slide at left) and a maximum right side (slide at right), with all the intermediate positions available, as shown in Figure 33.
Vertical Position
Allows to select the vertical position of the Orientation Tool, between a maximum lower side (slide at left) and a maximum upper side (slide at right), with all the intermediate positions available, as shown in Figure 33.
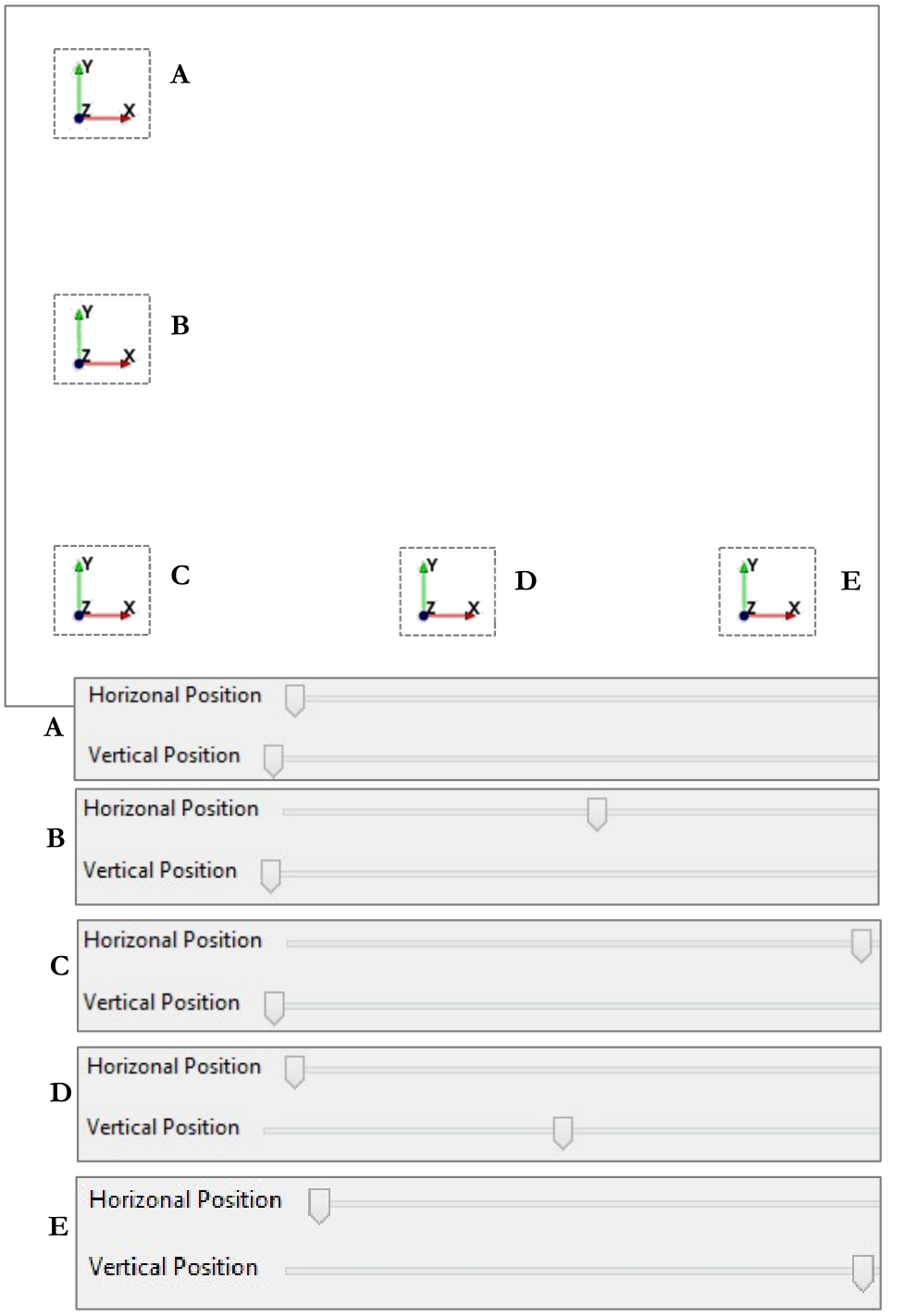
Figure 33 Different positions of the Orientation Tool Icon in the 3D scene panel
View Cross
If it is checked, the little white cross at the centre of the scene is visible, otherwise it is not.
View Mouse Indicators
If it is checked, the area ( see Figure 8 ) clicked with the mouse in the main 3D area will be highlighted, other it will be not drawn. If the user wants to record the video during the exploration of the current 3D scene then disable this flag can be useful.
View Picker settings
Is a very useful tool, which we will recall many times in this manual, because it is useful in more than one case. The “picker” is a black point which follows the cursor when it moves in 3D space. It lets the user know the coordinates of the position occupied by the cursor in real time. To insert a point in the 3D scene and to save the coordinates of one picked point open the settings by clicking on the View Picker setting button, the proper panel will appear (Figure 34):
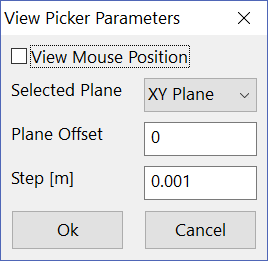
Figure 34 Picker Tool Panel
The same tool is also on the main toolbar of the 3D scene.
View Mouse Position
Is enabled when checked, a black point, which follows the cursor around, will appears in the 3D scene.
At the same time the X, Y and Z coordinates will appear at the bottom of the 3D scene. Clicking with the right mouse button in the 3D scene, while this tool is activated, the coordinates of the position occupied by the cursor in that moment are saved and the point remains fixed in the scene until a new point is picked. At the bottom of the 3D scene the stored coordinates are shown as “Last Picked X, Y, Z”, together to other information like the distance between the two points or the angles between them.
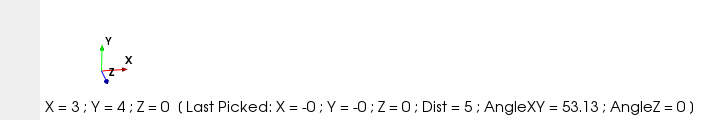
Figure 35 Mouse position
Select plane
Lets the user choose the plane on which the point will appears, through a pop-up menu as shown in Figure 36.
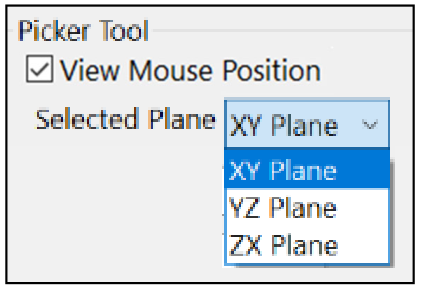
Figure 36 Picker Tool_Select Plane
In many cases it can be useful to disable the prospective during the mouse position analysis to avoid parallax problems; also an setting a view that is orthogonal to the picking plane used can help (see Camera options). To make the picking correctly, the plane chosen in this menu should match the view currently visualized in the 3D scene.
Selecting the “XY Plane”, “YZ Plane” and “ZX Plane” the main 3 orthogonal planes will be used to pick the mouse position. Selection the last option, “Objects”, the picking process is performed using the 3D object the mouse cursor is hovering over, providing a generic location independent from the three main planes.
Plane offset
The Picker Point moves on a 2D plane, the third dimension is set to 0 by default. Through this tool the user can change this value and to define a value for the third dimension, the position of the point in the direction perpendicular to the selected plane.
In the following example (Figure 37), a cube is inserted in the scene, with a Zmax of 3m; the selected plane is XY. So the X and Y coordinates are readable directly on the axes. The plane offset in this case determines the Z coordinate, which is 0 in one case and 3 in the other. To make the point visible, the Z of the picker must be equal or higher than the Z coordinate of the examined object (otherwise it goes under the object and it is not visible).
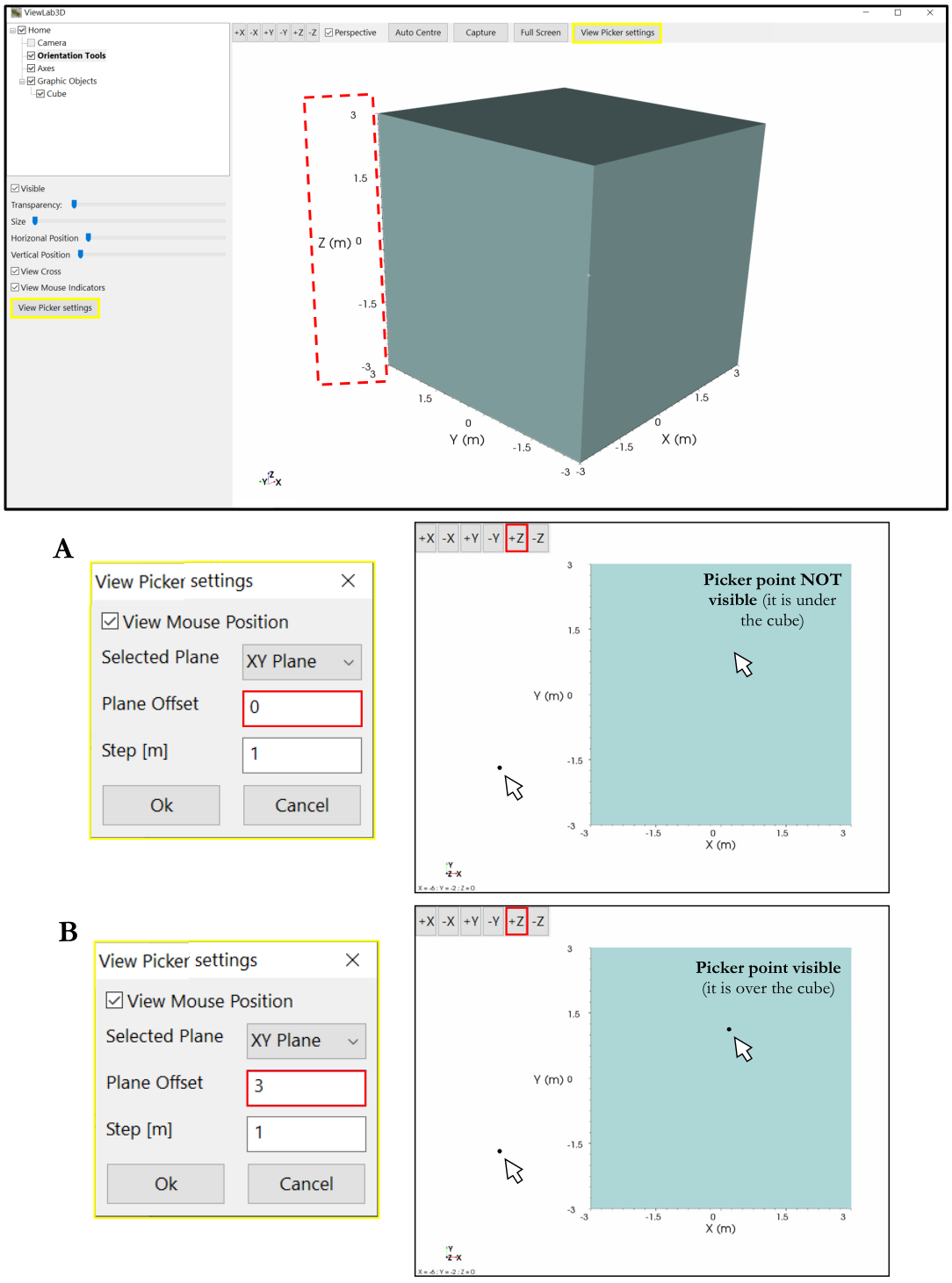
Figure 37 Plane offset of Picker Point
Step
This tool helps to insert a point at defined values of X and Y coordinates or a sequence of points at a certain interval distance. The number set in this box is the step with which the point moves in the 3D space. To make it move smoothly, set this number at very low value (0.001m by default). To make it move a defined interval value (e.g. 0.5m in Figure 38), write this number in the proper box and the point will move from its position to the next just when the cursor will be moved at least the defined distance.
In the following example (Figure 38), in A the step is 0.001m, so moving the cursor from X = 0 to X = -0.5, in the direction suggested by the red arrow, the pointer follows the cursor smoothly and in B the step is set to 0.5 so the point moves directly from X=0 to X=-0.5, in one single step.
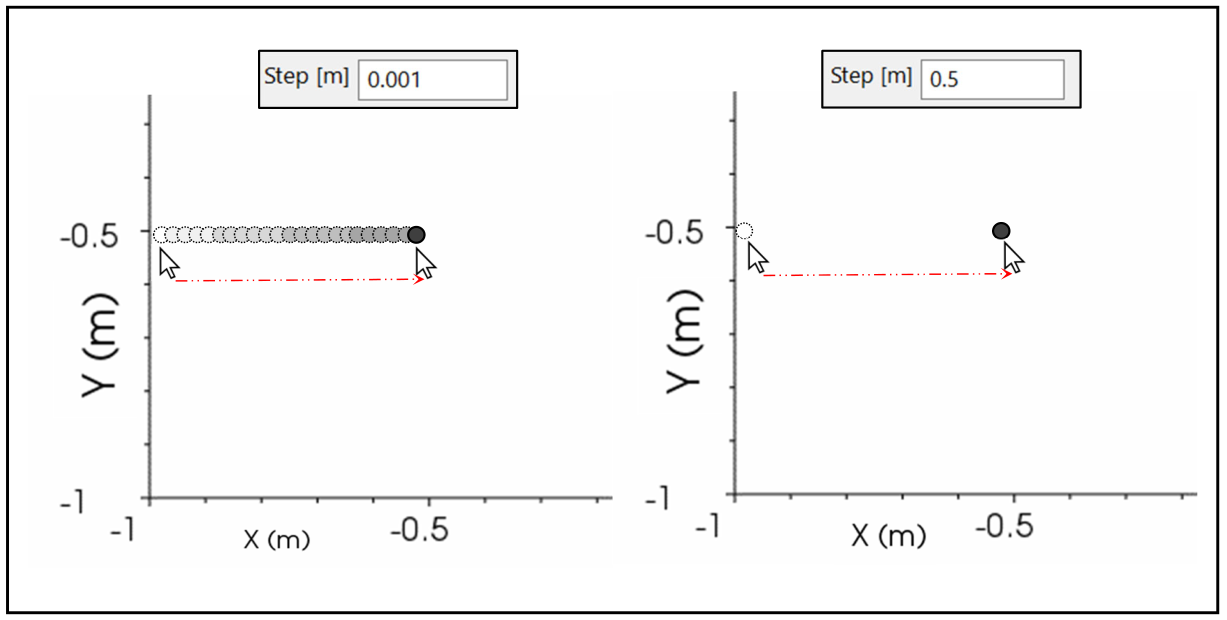
Figure 38 Different Steps of Picker Point
Mouse Position
Once the Picker Tool is set, it can be used to read the coordinate in real time, to insert electrodes through the direct interaction of the user with the scene (see Continuous mouse append), or simply to obtain the coordinates of a specific point in the 3D scene. This is the case in the following example where an object was inserted in the 3D scene (house). The selected point of view is +Y, so it is necessary to select the XZ plane in the picker point setting panel. It is advisable to uncheck the perspective view. Clicking with the right mouse button on the top right of the house, the proper coordinates are saved and they appear at the bottom of the screen (Figure 39).
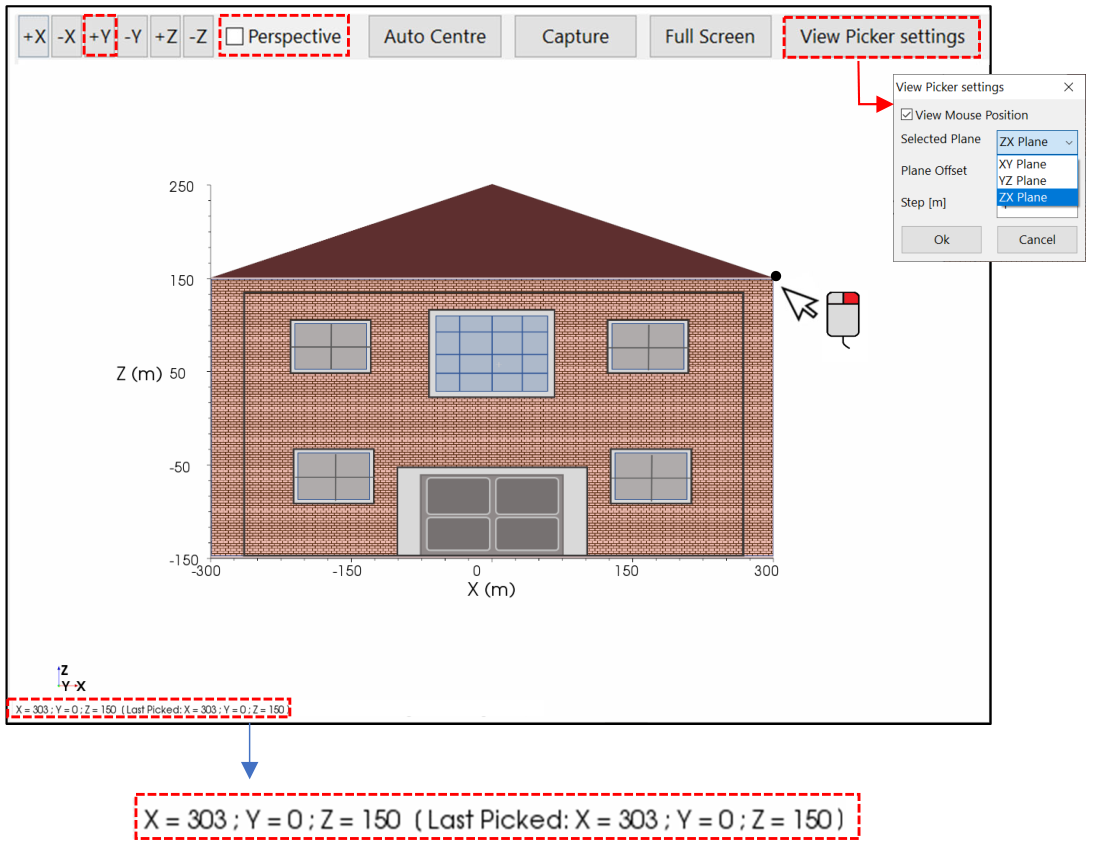
Figure 39 Example of coordinates obtaining