Measurements Tools
Right clicking on the node the “Measurements” option, a panel will appear with the available tools (Figure 225).
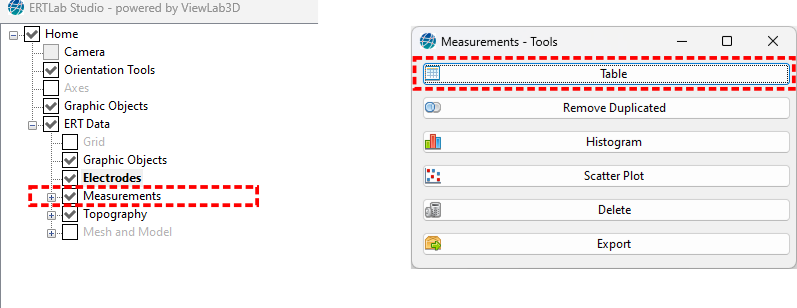
Figure 225 Measurements tools panel
All the options are explained in detail in the following sections.
Table
This table contains all available measurements. In contrast to the electrode table, this table is read only.
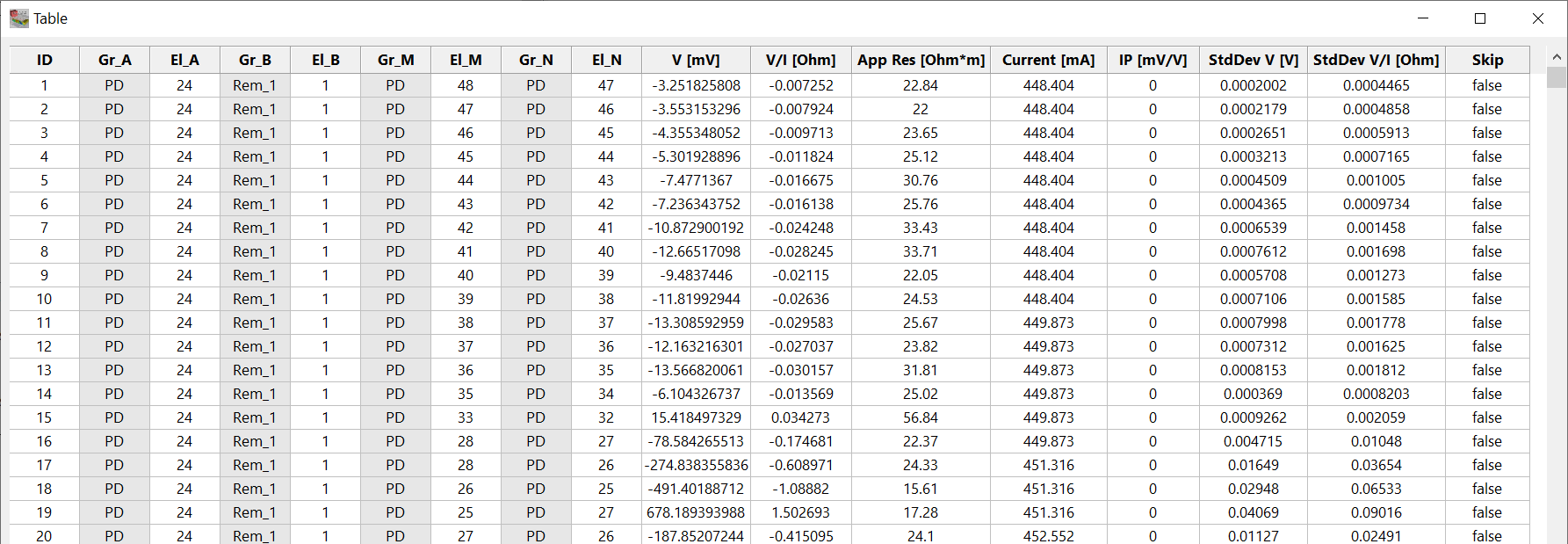
Figure 226 Measurements table
Opening the table shows the following columns:
ID: Identification Number;
Gr_A: Name of the group to which the electrode A belongs;
El_A: Number of electrode A;
Gr_B: Name of the group to which the electrode B belongs;
El_B: Number of electrode B;
Gr_M: Name of the group to which the electrode M belongs;
El_M: Number of electrode M;
Gr_N: Name of the group to which the electrode N belongs;
El_N: Number of electrode N;
K [m]: Geometrical Factor;
V [mV]: Electrical Potential;
V/I [Ohm]: Resistance;
App Res [Ohm*m]: Apparent Resistivity;
Current [mA]: Current between El_A and El_B;
IP [mV/V]: Induced Polarization;
Standard Deviation V[V]; Standard deviation of Electrical Potential;
Standard Deviation V/I [Ohm]; Standard deviation of Resistance;
Skip: if it is “true”, the data is not used for the inversion, but it is not deleted from the dataset memory.
Further options are available right clicking and choosing “Show All” (Figure 227).
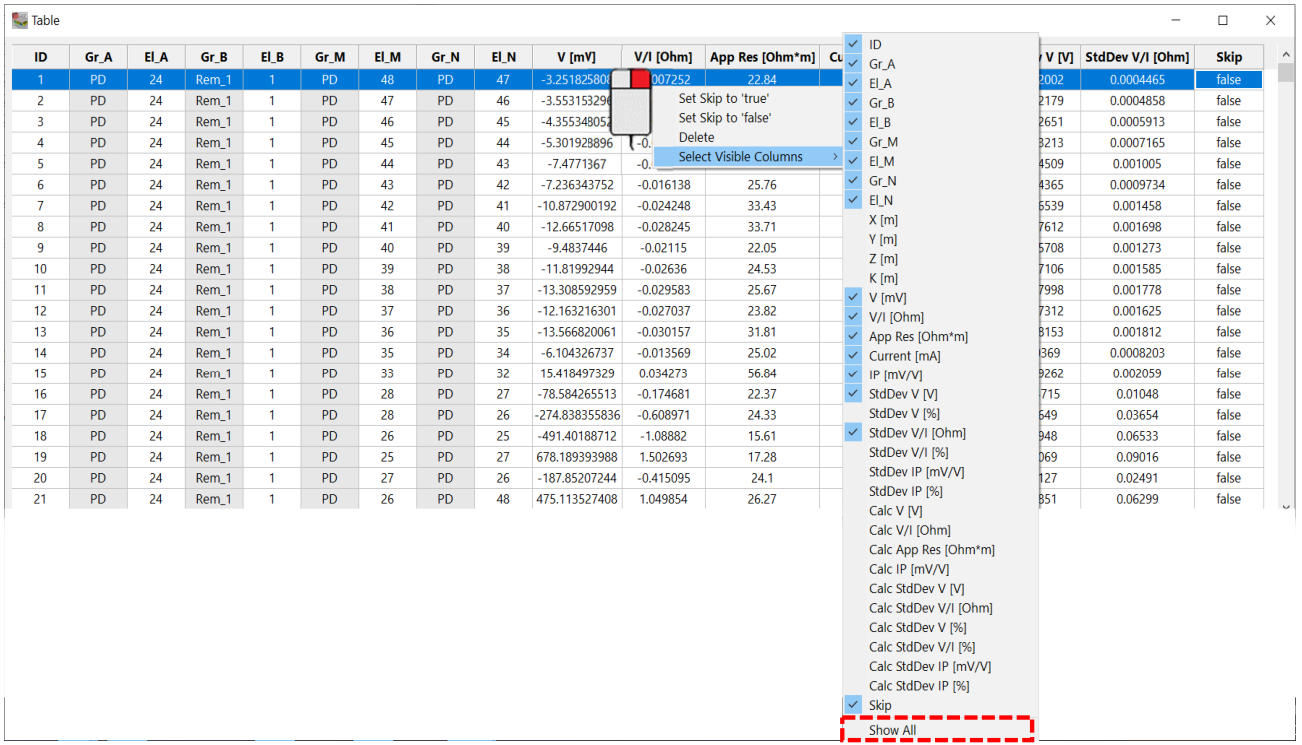
Figure 227 Show all visible columns
X [m]: X Coordinate of the electrode;
Y [m]: Y Coordinate of the electrode;
Z [m]: Z Coordinate of the electrode;
StdDev V [%]: Standard Deviation of Electrical Potential in percentage;
StdDev V/I [%]: Standard Deviation of Resistance in percentage;
StdDev IP [mV/V]: Standard Deviation of Induced Potential;
StdDev IP [%]: Standard Deviation of Induced Potential in percentage;
Calc V[V]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Electrical Potential;
Calc V/I [Ohm]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Resistance;
Calc App Res [Ohm*m]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Apparent Resistivity;
Calc IP [mV/V]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Induced Potential;
Calc StdDev V[V]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Electrical Potential;
Calc StdDev V/I[Ohm]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Resistance;
Calc StdDev V [%]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Electrical Potential in percentage;
Calc StdDev V/I [%]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Resistance in percentage;
Calc StdDev IP [mV/V]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Induced Polarization;
Calc StdDev IP [%]: Post Inversion/Post Forward Model Induced Polarization in percentage.
Left clicking on one of the column headings sorts all data in increasing order of that column. Left clicking a second times on the same column will sort the data in decreasing order.
Figure 228 shows an example where data are sorted by increasing Apparent Resistivity.
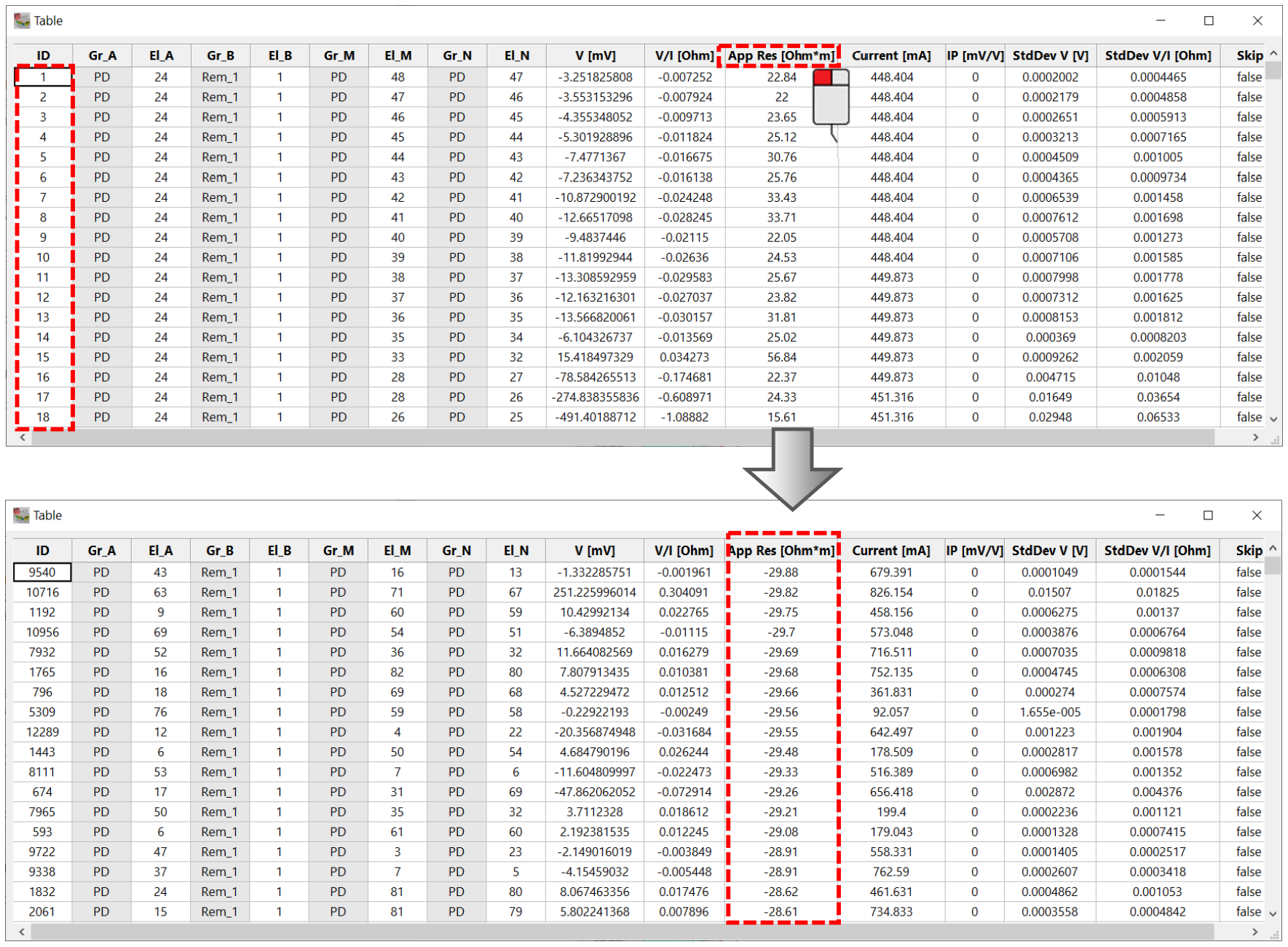
Figure 228 Sorting of Measurements Table. By default, it is sorted by increasing ID
Right clicking on any point of the table allows the user to:
Set skip to true: in this way the quadrupole is not used for the inversion, even if it is not deleted from the data file;
Set skip to false: in this way the quadrupole is used for the inversion; by default, all quadrupoles are set to “false”;
Delete: deletes the selected data from the project.
It is possible to do multiple selections by left clicking in the first and last row of the wanted selection and holding the SHIFT button all the lines between clicking (Figure 229).
To Skip (or unkip) a measurement it is also possible to simply double click the related row in the table.
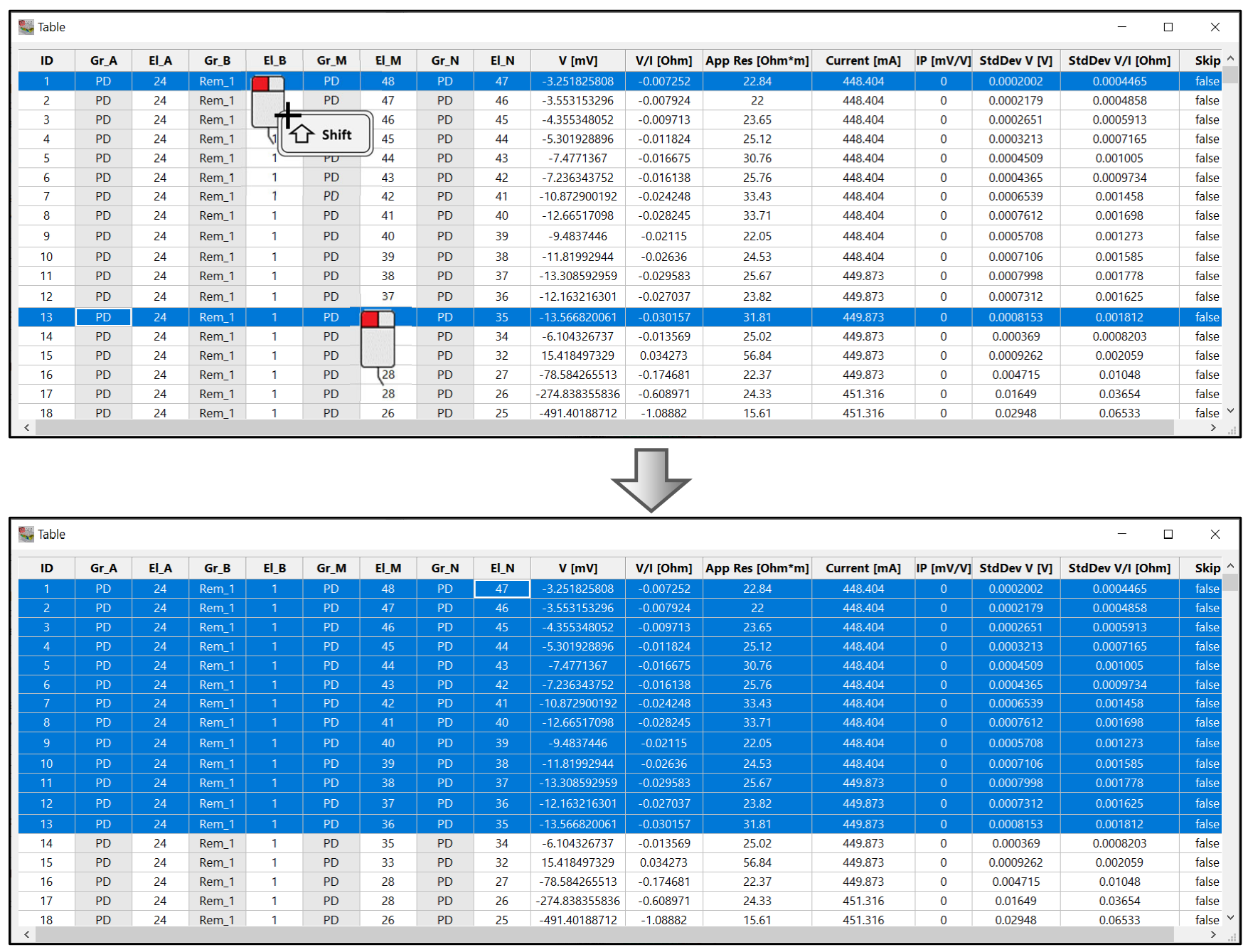
Figure 229 Sequential selection
Otherwise, to select more than one line, but in a non-sequential order, click on the desired lines and hold the Ctrl button (Figure 230):
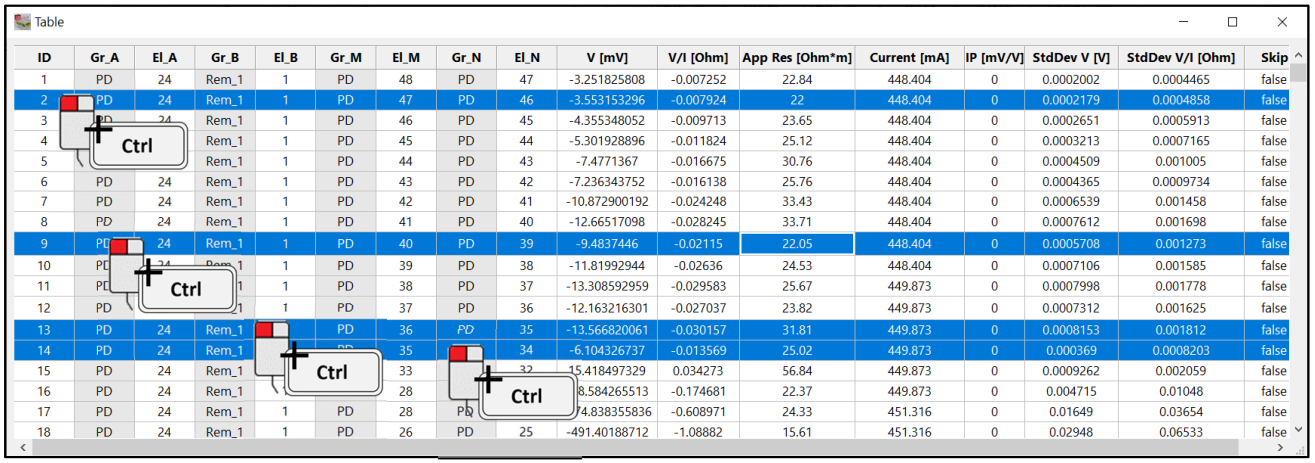
Figure 230 Non-sequential selection
Remove Duplicated
This tool allows the removal of duplicate and reciprocal measurements.
Figure 231 Remove duplicated Panel
Reciprocal Measurements have Transmitters (Tx, AB) and Receivers (Rx, MN) reversed. Theoretically, they should give the same measure. Schematically, in a quadrupoles AB_MN the following combinations are possible:

After clicking on the Remove Duplicated button and at the end of the computation, a message window will appear with information about the number of reciprocal quadrupoles and the difference of percentage average of Apparent Resistivity (Figure 232).
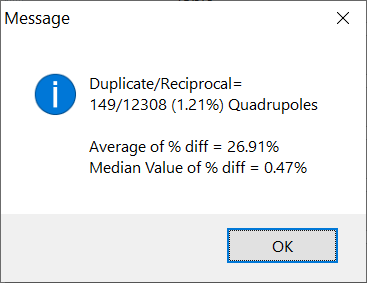
Figure 232 Duplicate/Reciprocal message
After clicking on Ok button, a new window will open, providing the user with three choices on what to do with the duplicated/reciprocal measurements. Options are:
Export Report to CSV: exports a .CSV file with information about duplicate/reciprocal measurements.
Set as Noise: the duplicate/reciprocal measurements are attributed to the Rho noise % in the inversion (section Data Error).
Remove Duplicated: deletes the duplicate/reciprocal measurements from the dataset.
Keep only Duplicated: to remove all measurement from the dataset that is not a duplicate/reciprocal measurements.
Remove only bad measurement: to remove duplicate/reciprocal measurement from the dataset that has an high deviation.
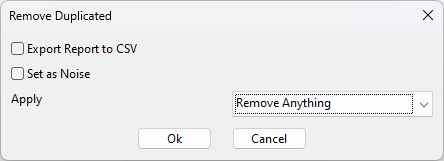
Figure 233 Remove Duplicated Measurements
Histogram
With this tool it is possible to visualize the measurements as Histograms, to have an easier representation of data distribution.
Figure 234 Histogram panel
This window has the tools to manage and visualize the data as histograms.
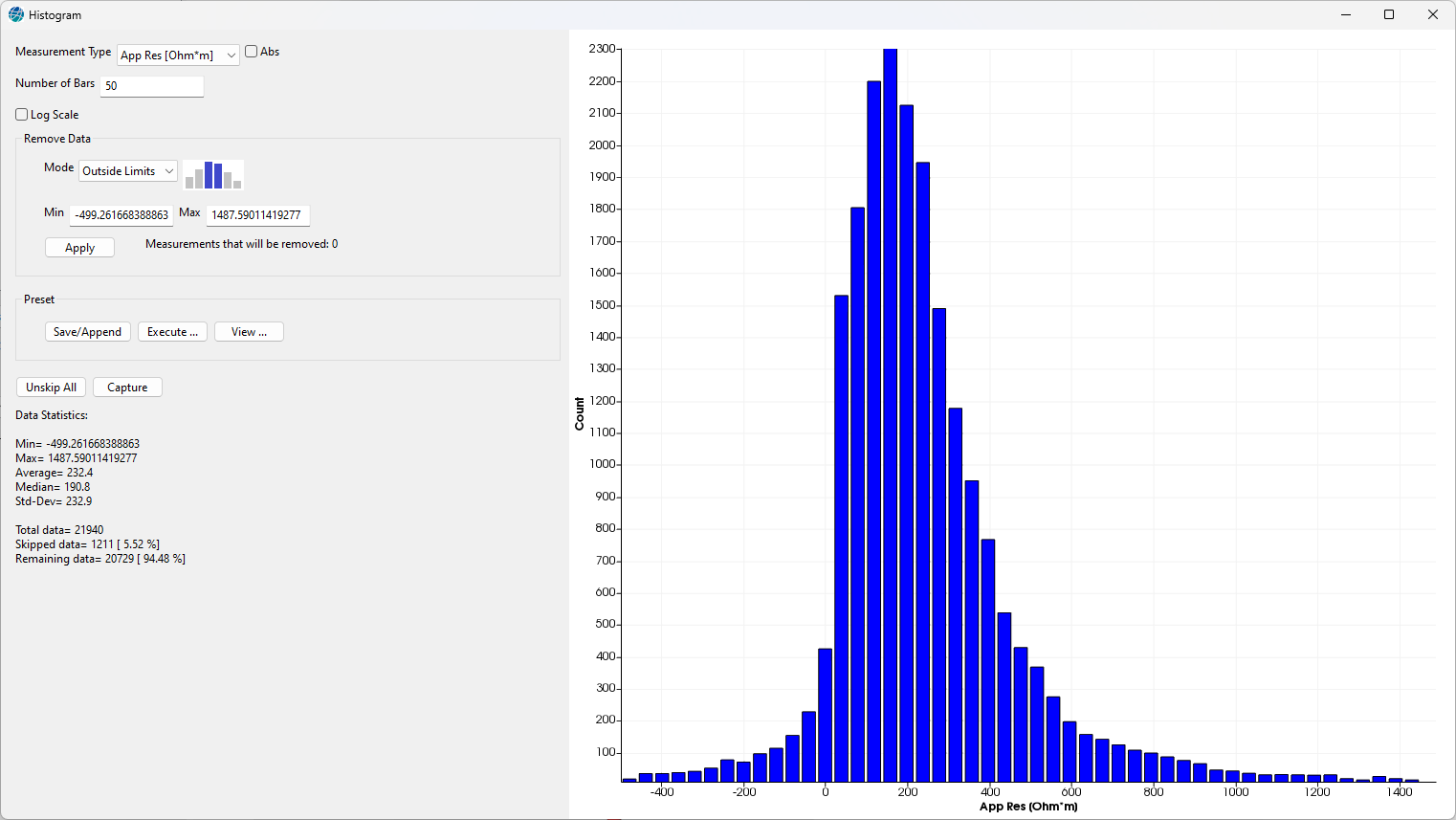
Figure 235 Histogram panel
Measurement Type
Choose the type of measurement, to be visualize in a histogram:
V/I [Ohm]
Apparent Resistivity [Ohm*m]
IP [mV/V]
K [m]
V [mV]
I [mA]
Standard Deviation V/I [Ohm]
Standard Deviation V[V]
Standard Deviation IP [mV/V]
Standard Deviation IP [%]
Calculated V/I [Ohm]
Calculated Apparent Resistivity [Ohm*m]
Calculated IP [mV/V]
Calculated Standard Deviation V/I [Ohm]
Calculated Standard Deviation IP [mV/V]
Calculated Standard Deviation IP [%]
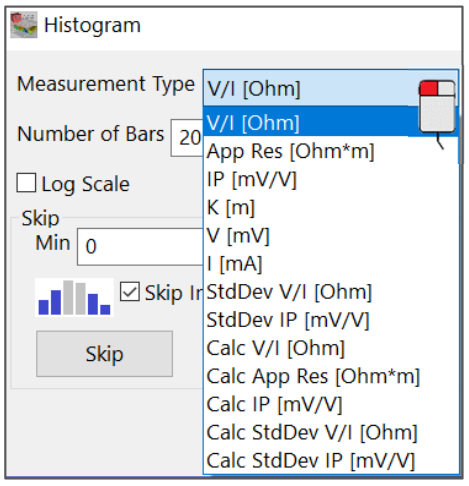
Figure 236 Choice of measurements to display as histogram
Number of Bars
The user has the option to change the number of bars’ for the histogram and set the logarithmic display mode for a better data distribution representation. In the following examples the histogram represent the V/I measurement with linear display mode (Figure 237 A), logarithmic display mode with 20 bars (Figure 237 B) and logarithmic display mode with 50 bars (Figure 237 C).
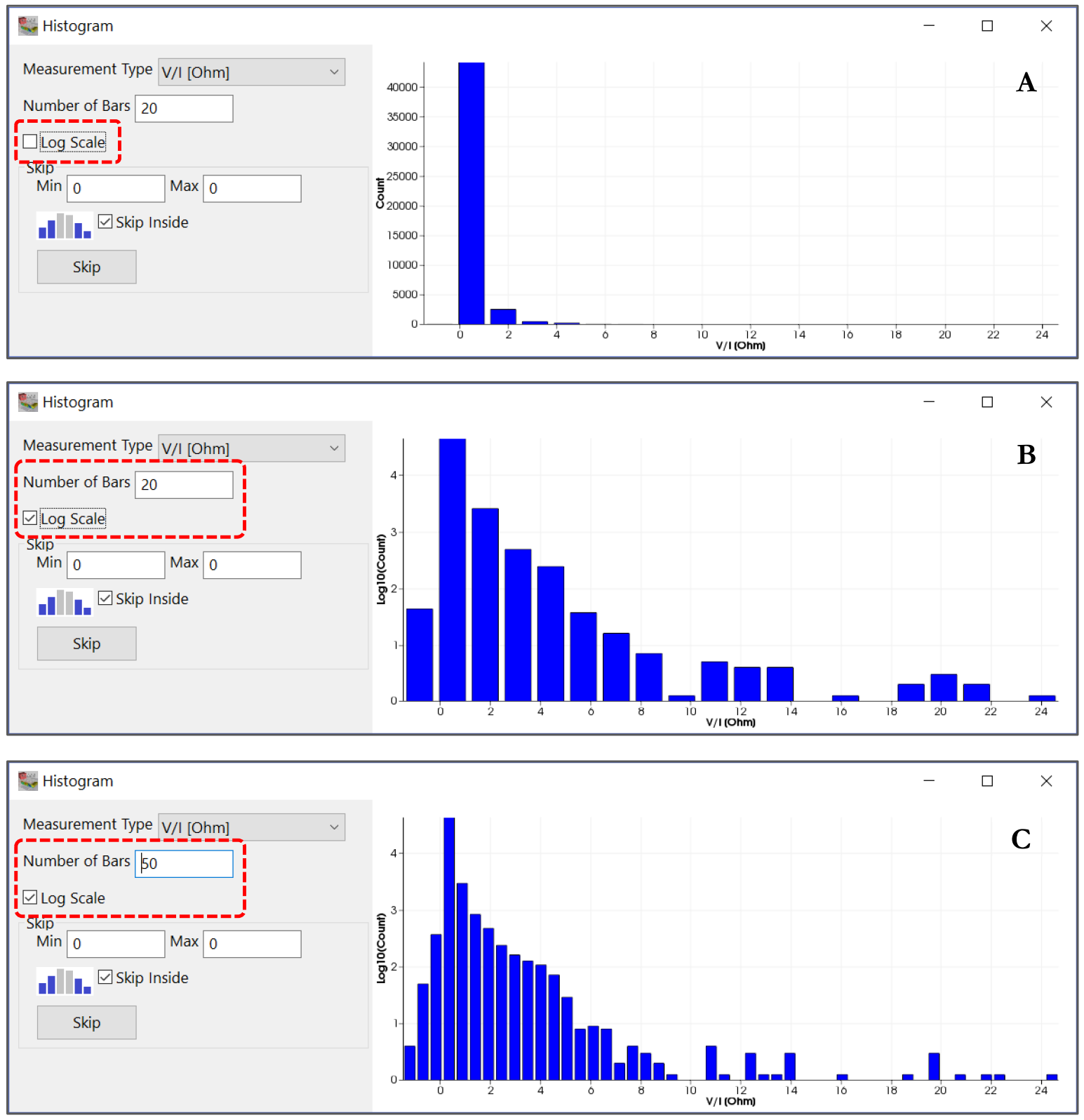
Figure 237 Logarithmic and number of bars setting
Mode
Select outside limits to filter the data externally to the selected cut limit values and preserve the internal data. Otherwise, by selecting inside limits data inside the cut limits are filtered. In Figure 238 the data range is set to -1 as minimum value and to 9.5 as maximum value. In the first case the measurements outside the limits are skipped, in the second case those internal.
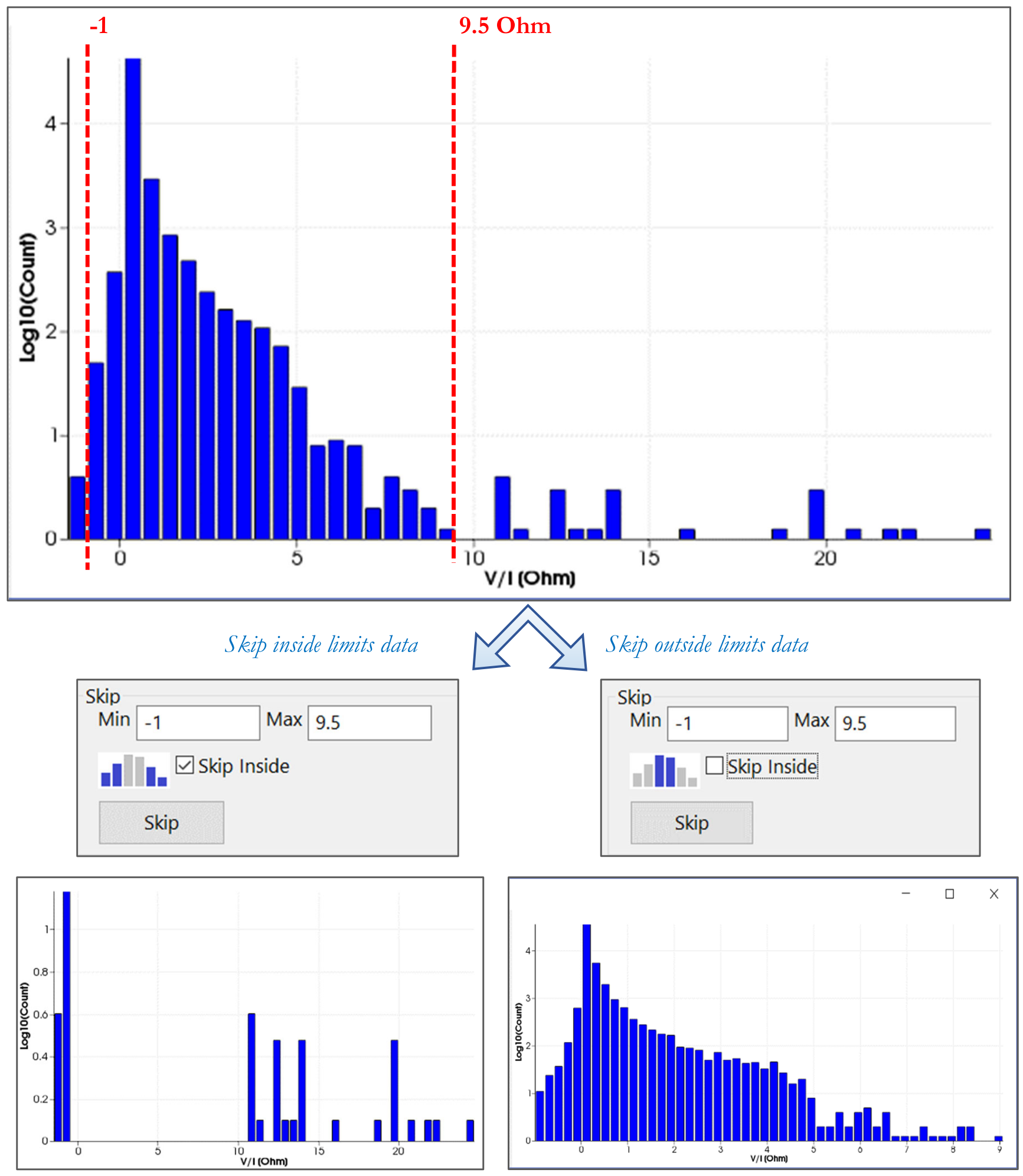
Figure 238 Filtering Outside/Inside limits data
Min Max
Examine the amount of filtered data after the application of your filter choices in the Statistical Summary panel, where the Minimum and Maximum values of the dataset, the Average and Median values, the total number of measurements, and the number of skipped data are reported.
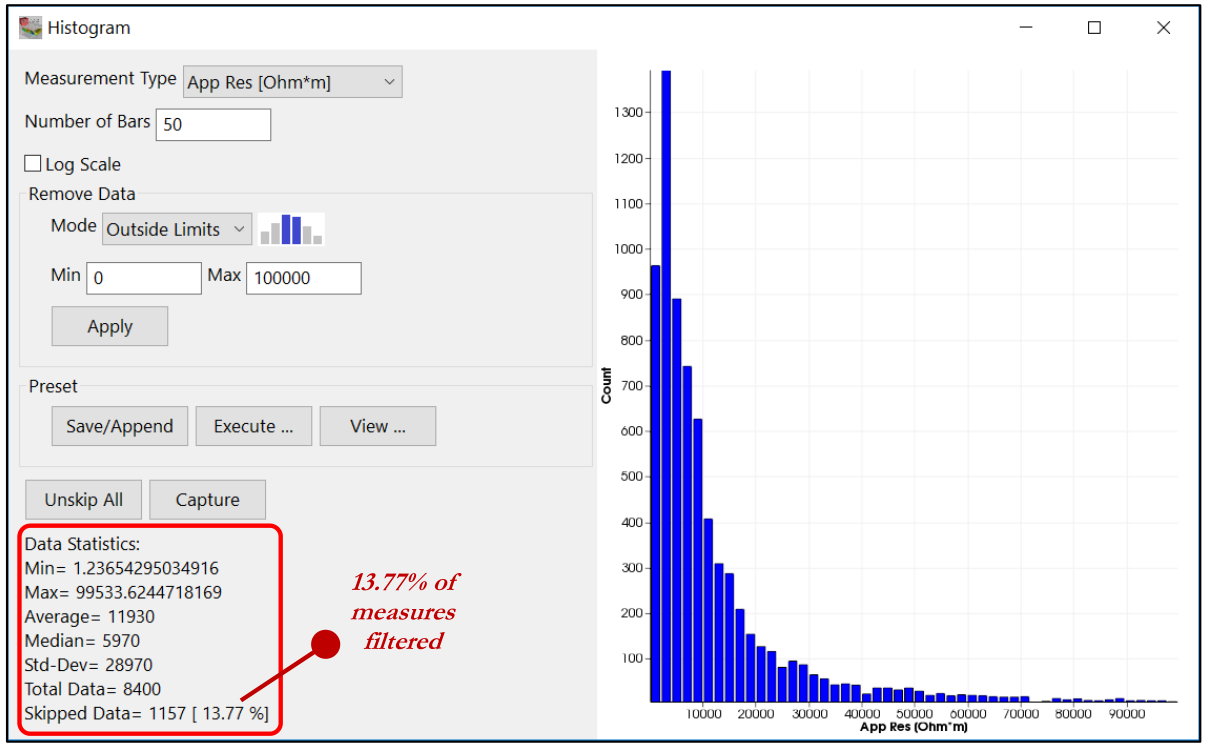
Figure 239 Data Statistics in Histogram Panel
Note that this values can be also graphically set with the use of the mouse (and its left button).
Apply
After that the filtering parameters are set, then it is possible to Apply the process pressing this button.
An estimation of the number of measurement that will be removed it is written at the right of the button.
The filtered data are not deleted only excluded from the inversion processing. The table is automatically updated and the filtered data are greyed out (Figure 240).
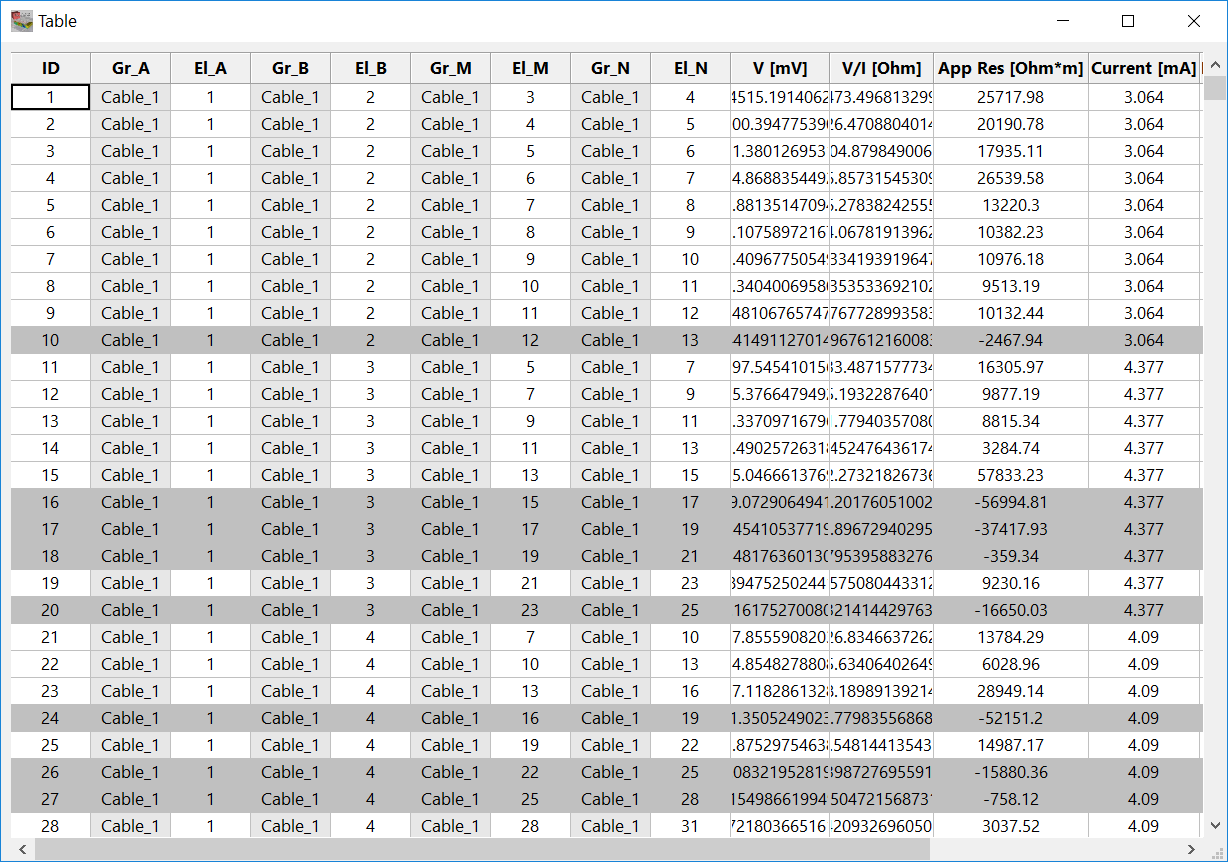
Figure 240 In grey, filtered measurement
However, it is possible to delete them from the project (see section Delete).
Preset
If some filter is commonly used, or a sequence of them is frequent, then it can be saved and recalled with a quicker procedure.
First it is necessary to set the parameter of of the filter (see Measurement Type, Mode and Min Max). After this in place of press the button Apply press the button “Save/Append”. Because more Preset can be specified then the name needs to be specified.
After the the filter(s) are specified it is then later possible to execute it pressing the button “Execute…”; it will be asked also the the name of the preset to be run.
Pressing the button “View…” it is possible to examine an already saved Preset, to possibly modify it also.
Unskip All
In case of problem it is possible to reset all the filtering steps and so to restore all the measurement in the dataset.
Capture
Pressing this button it is possible to save to file the current plot shown.
Scatter Plot
This option visualizes the measurements as X-Y dispersion plot, to have a graphical representation of data distribution.
Figure 241 Scatter plot Panel
In this window two measurements can be visualized as scatterplot.
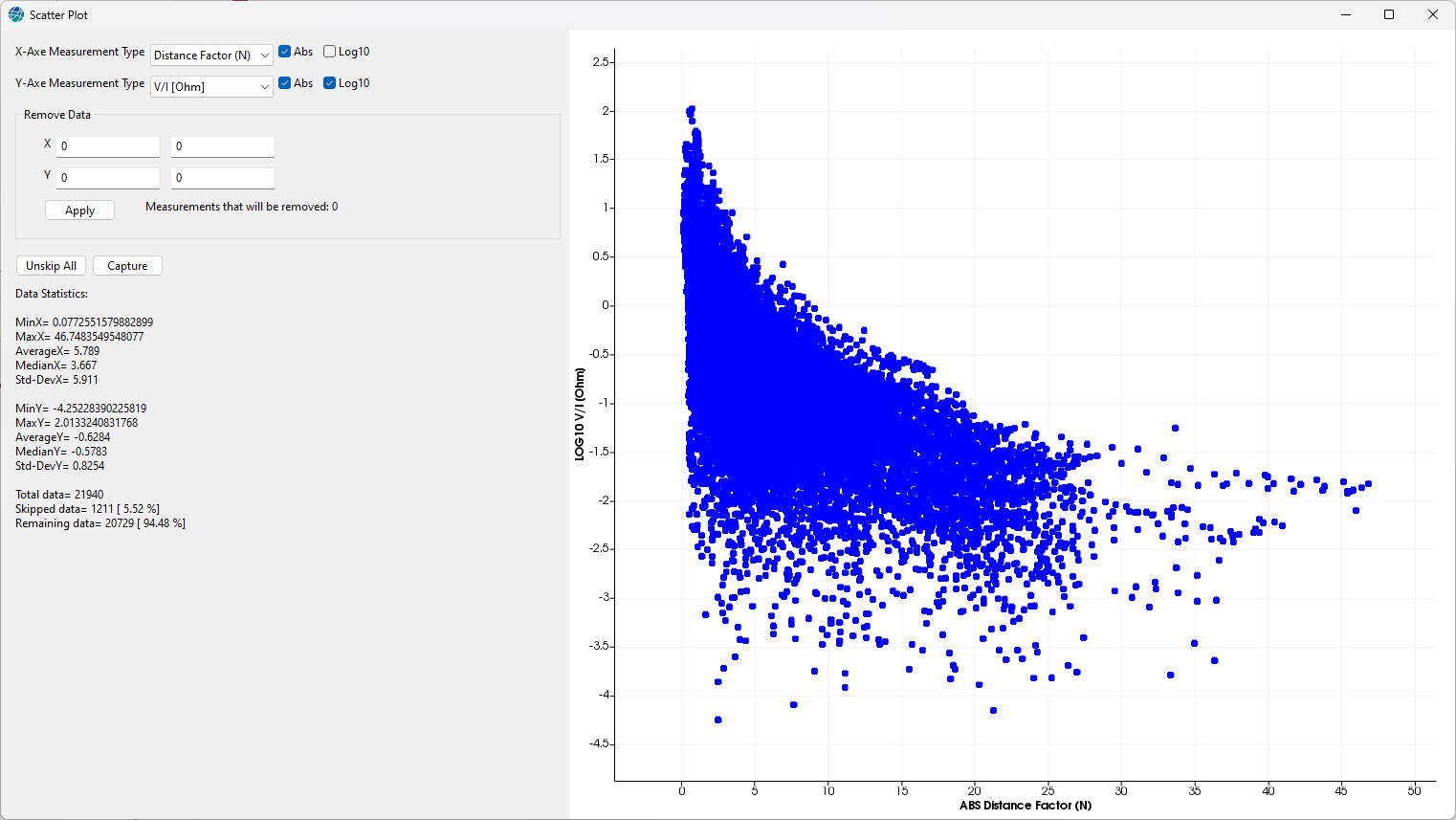
Figure 242 Scatter plot
On the left side the two types of measurements to display can be selected, one for the X-axis and one for the Y-axis. Click in the dropdown boxes for the possible selections, which are:
V/I [Ohm]
Apparent Resistivity [Ohm*m]
IP [mV/V]
K [m]
V [mV]
I [mA]
Standard Deviation V/I [Ohm]
Standard Deviation V[V]
Standard Deviation IP [mV/V]
Standard Deviation IP [%]
Calculated V/I [Ohm]
Calculated Apparent Resistivity [Ohm*m]
Calculated IP [mV/V]
Calculated Standard Deviation V/I [Ohm]
Calculated Standard Deviation IP [mV/V]
Calculated Standard Deviation IP [%]
ID
EI A ID
EI B ID
EI N ID
X
Y
Z
Remove Data
Here can be set a range of values (both in terms of X and Y axes) where the filter will remove the inner measurements.
Note that this values can be also graphically set with the use of the mouse (and its left button).
Apply
After that the filtering parameters are set, then it is possible to Apply the process pressing this button.
An estimation of the number of measurement that will be removed it is written at the right of the button.
Unskip All
In case of problem it is possible to reset all the filtering steps and so to restore all the measurement in the dataset.
Capture
Pressing this button it is possible to save to file the current plot shown.
Delete
This option allows to delete some measurements. Click on the Delete button; an information window will show the total number of measurements and the number of filtered measurements.
Figure 243 Delete measurements button
Note, if there are no filtered data, clicking on OK button will delete all the data (Figure 244).
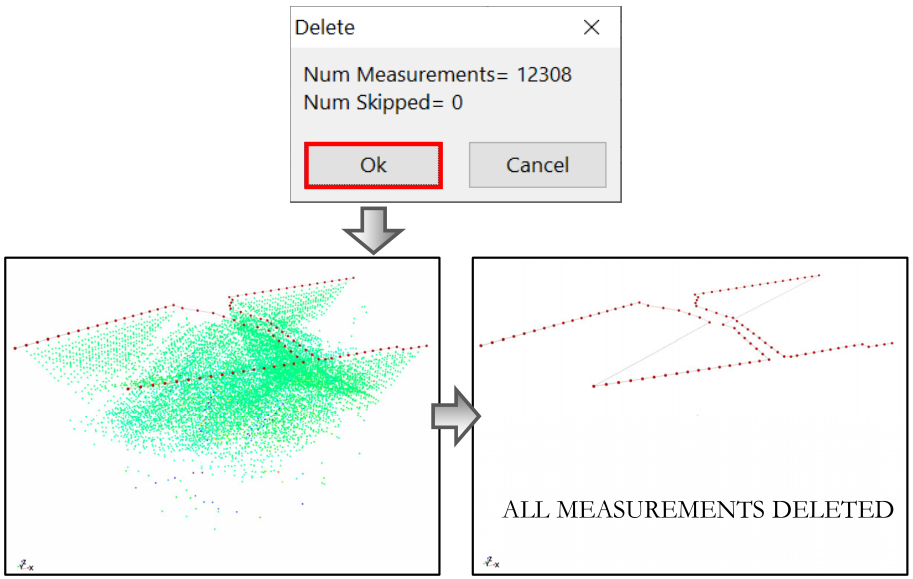
Figure 244 Delete measurement with no skipped data
On the contrary, if some filtered data are present one can choose to delete them or those remaining (Figure 245). Clicking on the OK button deletes the measurements from the dataset.
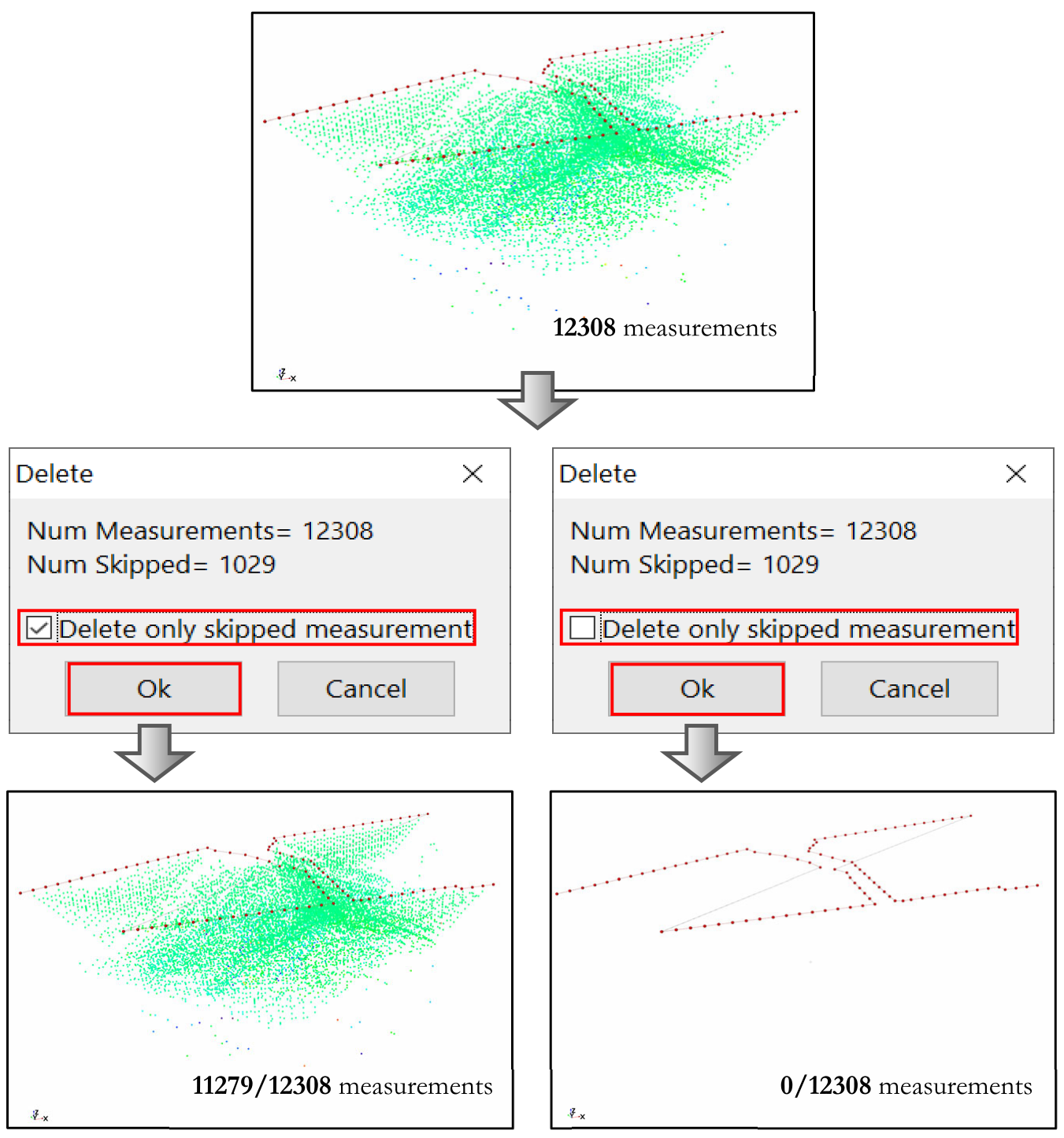
Figure 245 Remove measurements with skipped data
Export
Through this option it is possible to export a .txt file with information about electrodes and measurements.
Figure 246 Export button
The saved file is a .txt file where the first part shows the coordinates of the electrodes and in the next part the electrodes that constitute the quadrupole ABMN of each measurement (Figure 247).
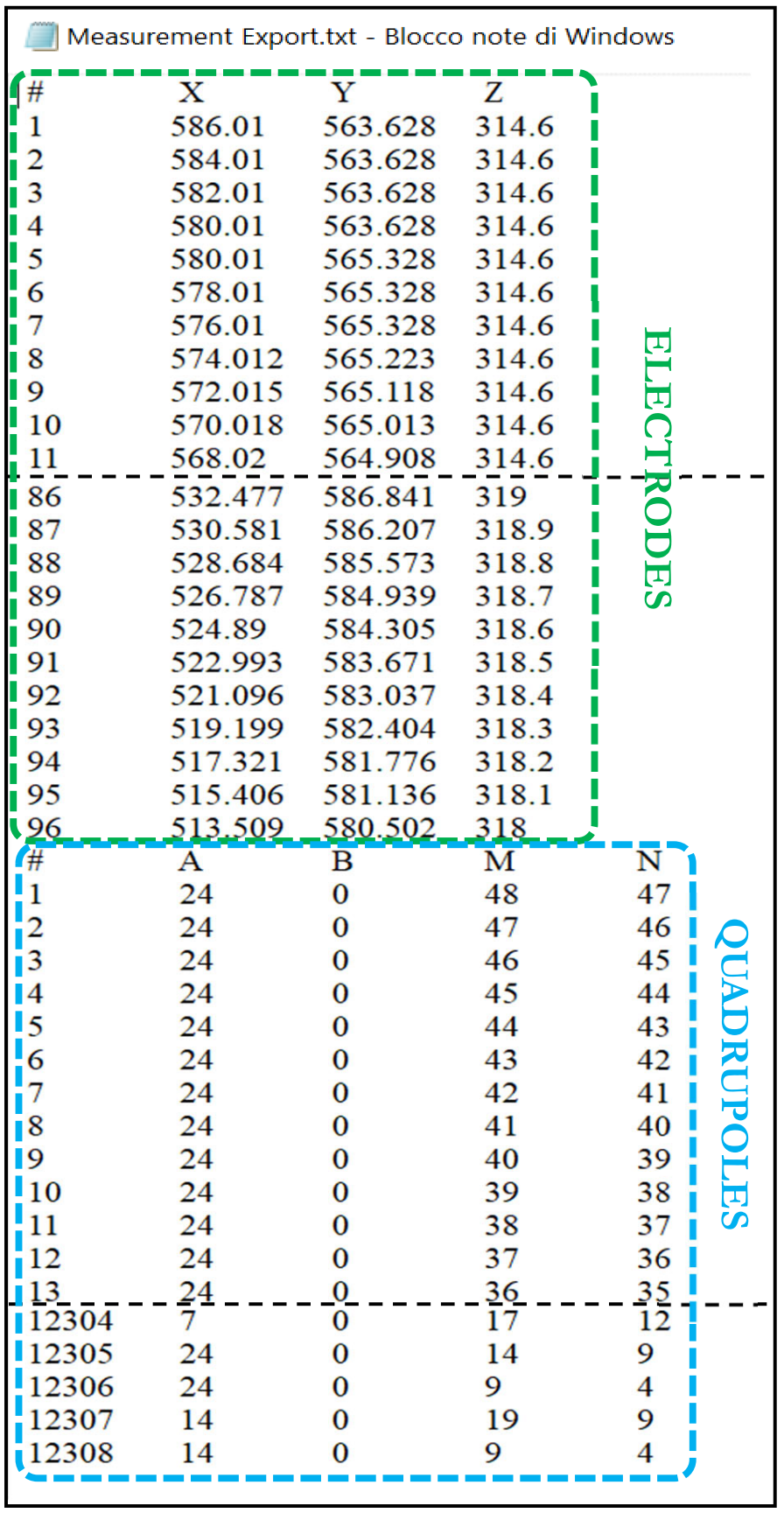
Figure 247 Export measurements table